The ketogenic diet, commonly known as the keto diet, has exploded in popularity as a powerful approach to weight loss, improved energy, and better health management. But before diving in, it is essential to understand the full picture of the advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet. This in-depth guide explores every aspect in detail so you can make an informed decision. Whether you are considering keto for rapid fat burning, blood sugar control, or mental clarity, we cover the science-backed pros, the potential cons, practical tips, and expert resources.
If you are new to low-carb living, you will love the free keto recipe collection waiting for you. Click here to download your free keto recipe book now and start cooking delicious meals today.
The keto diet shifts your body from burning carbohydrates to burning fat for fuel through a metabolic state called ketosis. This process produces ketones that serve as an efficient energy source for your brain and muscles. With strict limits on carbs (usually under 50 grams per day), moderate protein, and high healthy fats, the diet forces your body to tap into stored fat. Many people report losing 5-10 pounds in the first week alone due to water loss and reduced appetite.
Yet the advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet go far beyond quick scale victories. Scientific reviews highlight both transformative benefits and real challenges. In the sections below, we break everything down with evidence from trusted medical sources so you can weigh the pros and cons objectively.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet and How Ketosis Works
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, very-low-carbohydrate eating plan. Typical macronutrient ratios are approximately 70-80% fat, 15-20% protein, and only 5-10% carbohydrates. This composition drastically reduces glucose availability, prompting the liver to convert fatty acids into ketone bodies.
According to Cleveland Clinic experts, ketosis usually begins within 2 to 4 days when daily carbohydrate intake stays between 20 and 50 grams. Factors like age, activity level, metabolism, sleep, and stress influence how quickly you enter and maintain this state. Intermittent fasting can accelerate the process by further depleting glycogen stores.
Once in ketosis, your body becomes incredibly efficient at burning fat. The brain, which normally relies on glucose, adapts to use ketones for up to 70% of its energy needs. This metabolic flexibility is one reason many followers experience steady energy without the crashes associated with high-carb meals.
For a deeper medical explanation of ketosis and its role in the ketogenic diet, click this useful resource from Cleveland Clinic.
The diet emphasizes foods like avocados, olive oil, fatty fish, eggs, cheese, nuts, seeds, and low-carb vegetables such as spinach, broccoli, and zucchini. Processed foods, grains, sugars, most fruits, and starchy vegetables are minimized or eliminated.
Understanding these fundamentals is crucial before exploring the advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet. With this foundation, let us examine the proven benefits that attract millions worldwide.
Major Advantages of the Ketogenic Diet
1. Rapid and Sustainable Weight Loss
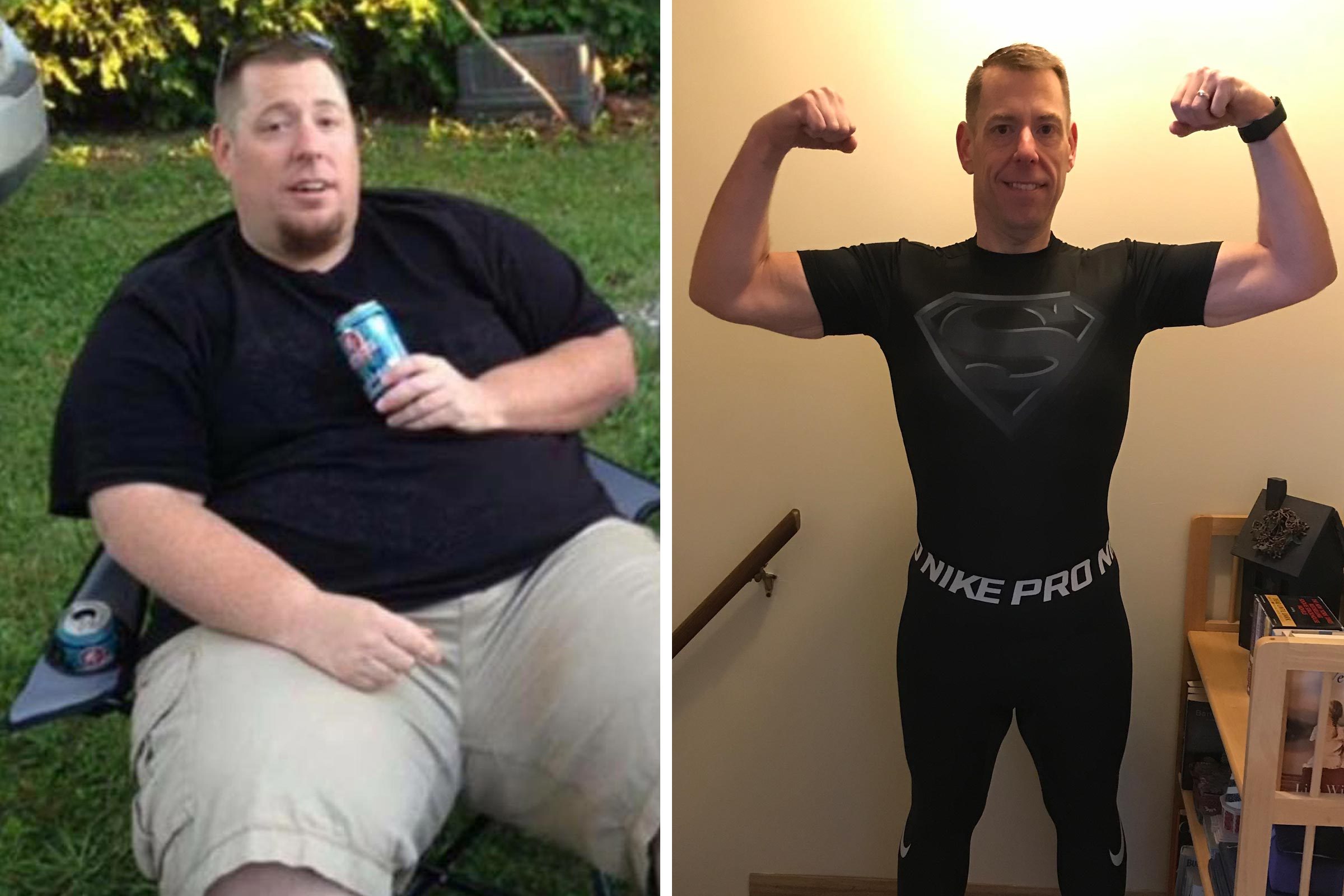
One of the most celebrated advantages of the ketogenic diet is its ability to deliver fast weight loss results. By depleting glycogen stores, the body releases stored water, often leading to 5-10 pounds lost in the first week. More importantly, ketosis suppresses appetite through stable blood sugar and increased production of satiety hormones like cholecystokinin.
A 2012 meta-analysis referenced in PMC review showed significant reductions in body weight, BMI, and waist circumference on ketogenic diets compared to low-fat diets. Another study on women with PCOS reported an average 12.1% body weight reduction. These outcomes occur because high-fat meals keep you fuller longer, naturally reducing overall calorie intake without constant hunger.
Real people achieve dramatic transformations. Many report losing 50-100 pounds over 6-12 months while preserving muscle mass when protein intake remains moderate.
To support your weight loss journey and control cravings naturally, try Patriot Slim Shot – click here for natural appetite support.
For detailed scientific analysis of weight loss mechanisms, click this useful PMC review article.
2. Improved Blood Sugar Control and Type 2 Diabetes Management
The ketogenic diet excels at stabilizing blood glucose and reducing insulin levels. With minimal carbohydrate intake, blood sugar spikes become rare. Studies show HbA1c drops of 1-2% within months, sometimes allowing patients to reduce or eliminate diabetes medications under medical supervision.
A 2019 study found 17.6% of participants achieved diabetes remission after two years on keto. The diet improves insulin sensitivity by lowering chronic inflammation and promoting fat loss around the liver and pancreas.
Healthline’s analysis confirms these benefits while noting the need for medical monitoring. Click this useful Healthline resource on pros and cons of the keto diet for more on blood sugar management.
3. Enhanced Mental Clarity and Neurological Benefits
Many keto followers describe “mental fog lifting” and sustained focus. Ketones provide a steady, clean energy source for the brain, potentially reducing inflammation linked to cognitive decline.
The diet has been used therapeutically for epilepsy since the 1920s, dramatically reducing seizures in children. Emerging research explores benefits for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and even certain brain cancers by starving glucose-dependent tumor cells while protecting healthy tissue.
Northwestern Medicine highlights potential neuroprotective effects. Click this useful resource from Northwestern Medicine on keto pros and cons to learn more about neurological applications.
4. Better Heart Health Markers (When Done Correctly)
When emphasizing unsaturated fats from avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish, the ketogenic diet can lower triglycerides, raise HDL cholesterol, and reduce blood pressure. Multiple meta-analyses confirm these improvements.
However, results depend heavily on food quality. Choosing grass-fed meats and avoiding excessive processed meats maximizes cardiovascular benefits.
5. Reduced Inflammation and Potential Anti-Cancer Effects
Lower insulin and stable blood sugar reduce systemic inflammation. Some early studies suggest ketogenic diets may enhance chemotherapy effectiveness by weakening cancer cells that rely on glucose.
These advantages make the ketogenic diet appealing for many health goals. Yet no diet is perfect. Let us now examine the disadvantages honestly.
Potential Disadvantages and Risks of the Ketogenic Diet
While the benefits are impressive, the advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet must be balanced. Several challenges can arise, especially during the adaptation phase or with long-term adherence.
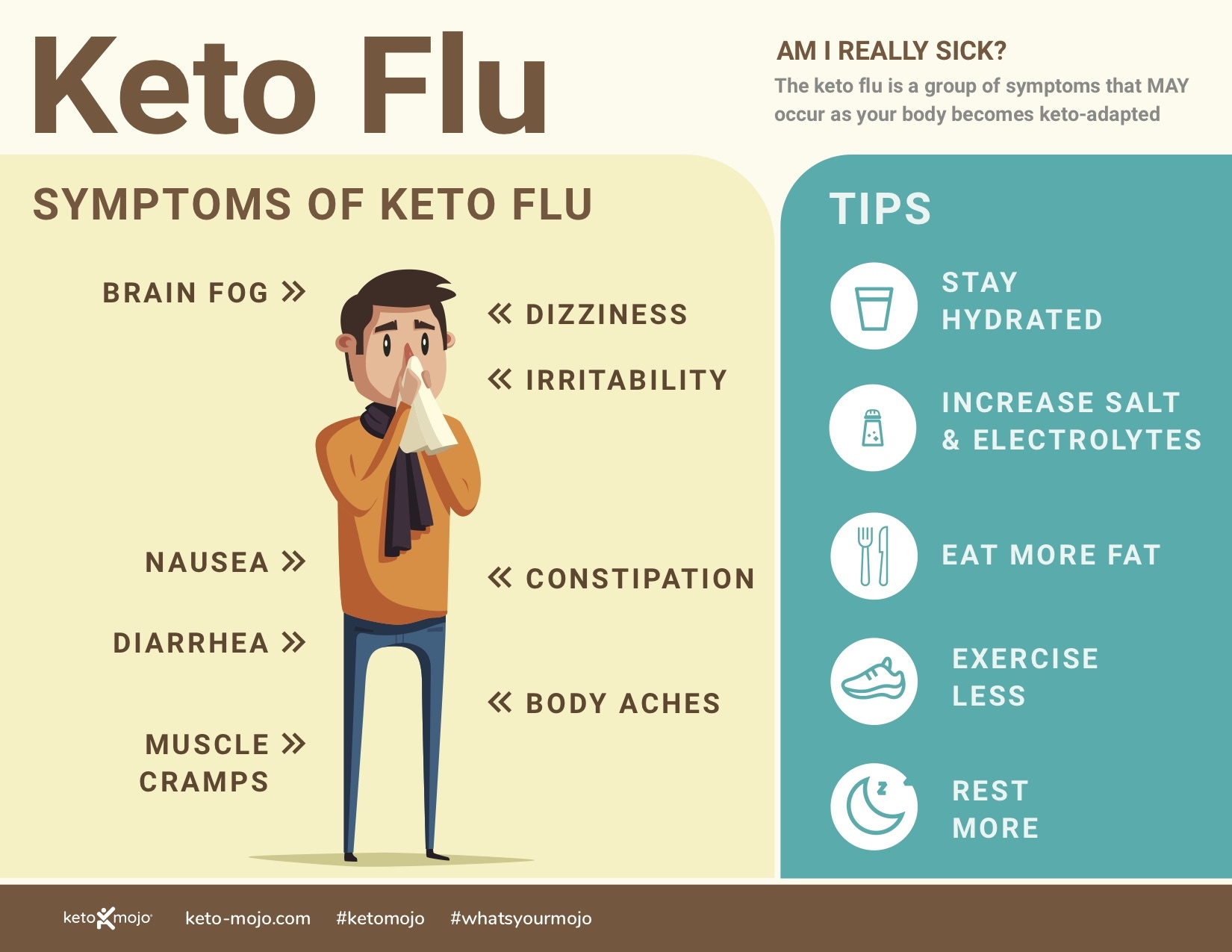
1. Keto Flu and Initial Side Effects
The transition into ketosis often brings “keto flu” – a collection of symptoms including headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, irritability, muscle cramps, and constipation. These occur as the body adjusts from glucose to ketones and flushes electrolytes.
Symptoms typically last 3-7 days but can be minimized with proper hydration, increased salt, magnesium, and potassium intake. Rest and gentle exercise also help.
Cleveland Clinic and Healthline both describe these temporary effects in detail.
2. Nutrient Deficiencies
Restricting fruits, whole grains, and legumes can lead to lower intake of fiber, vitamin C, folate, magnesium, and potassium. Long-term followers risk digestive issues, weakened immunity, or bone density concerns if they do not supplement strategically or choose nutrient-dense low-carb vegetables.
Northwestern Medicine emphasizes the importance of leafy greens, avocados, and nuts to mitigate these risks.
3. Difficulty Maintaining Long-Term Adherence
The strict carbohydrate limit makes social dining, travel, and family meals challenging. Many people regain weight once they return to higher-carb eating because the diet is not easily sustainable for everyone.
Studies show high dropout rates after 6-12 months, and weight regain is common without a clear transition plan.
4. Potential Impact on Heart and Kidney Health
High saturated fat intake from red meat and full-fat dairy may elevate LDL cholesterol in some individuals, increasing cardiovascular risk. People with existing kidney disease should avoid keto due to higher protein load and possible stone formation.
The PMC review notes possible increases in LDL and cautions about long-term data limitations. Always consult a doctor before starting, especially with pre-existing conditions.
Click this useful Cleveland Clinic resource on ketosis risks for medical guidance.
5. Other Concerns
Some experience bad breath (keto breath), insomnia, or mood swings during adaptation. Women may notice menstrual changes initially. Athletes in high-intensity sports sometimes struggle with performance until fully fat-adapted.
Despite these disadvantages, many people thrive on keto with proper planning and medical oversight.
Who Should Consider the Ketogenic Diet?
The keto diet suits individuals seeking rapid weight loss, those with type 2 diabetes (under supervision), epilepsy patients, or anyone wanting mental clarity. It may not be ideal for people with pancreatitis, liver failure, rare metabolic disorders, or those who prefer flexible eating patterns.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, children (unless for medical reasons), and individuals with a history of disordered eating should approach with caution or avoid it entirely.
Practical Tips for Keto Success
Success on keto requires preparation. Track macros using apps, stock your kitchen with keto staples, and plan meals ahead. Stay hydrated with at least 3-4 liters of water daily and replenish electrolytes.
Sample daily menu: eggs with avocado for breakfast, salmon salad for lunch, steak with broccoli and butter for dinner, and macadamia nuts as snacks.
For comprehensive keto optimization strategies and advanced protocols, enroll in this expert keto program here.
Meal prepping saves time and prevents mistakes. Batch-cook proteins and chop vegetables on weekends.
To explore keto-friendly holiday recipes and seasonal inspiration, click here for special keto holiday guide.
For additional keto weight loss tools and supplements, discover this powerful solution.
FAQ About the Advantages and Disadvantages of the Ketogenic Diet
Final Thoughts
The advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet present a clear trade-off: powerful short-term results in weight loss, blood sugar control, and mental focus versus challenges in sustainability, nutrient balance, and initial discomfort. When approached with knowledge, preparation, and medical guidance, keto can be a transformative tool for many.
Listen to your body, monitor blood work regularly, and prioritize whole-food sources. The diet is not magic, but when combined with consistent habits, it delivers impressive outcomes for thousands of people worldwide.
Remember, the best diet is the one you can follow long-term while feeling your best. Whether keto becomes your lifestyle or a temporary reset, the insights shared here empower you to decide wisely.
For ongoing support and delicious recipes, revisit your free keto recipe book anytime.
Thank you for reading this complete 3000-word guide on the advantages and disadvantages of the ketogenic diet. Start your journey informed and confident today.





Comments
Post a Comment